The following properties can be modified on the Connection properties pages:
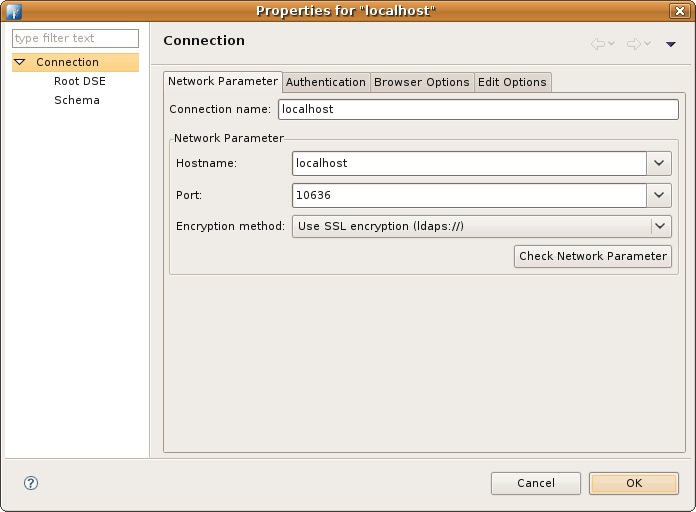
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection name | The name of the connection. In the Connections view the connection is listed with this name. The name must be unique. |
| Hostname | The hostname or IP address of the LDAP server. A history of recently used hostnames is available through the drop-down list. |
| Port | The port of the LDAP server. The default port for non-encyrpted connections is 389. The default port for ldaps:// connections is 636. A history of recently used ports is available through the drop-down list. |
| Encryption method | The encryption to use. Possible values are 'No encrypton', 'ldaps://' and 'StartTLS extension'. |
| Check Network Parameter | Use this function if you want validate that the entered information is correct and the server is reachable. |
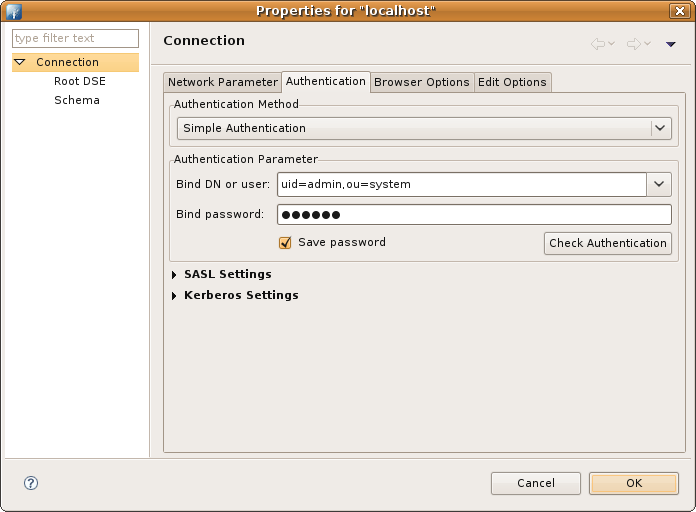
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Authentication Method |
Select your authentication method between:
|
| Bind DN or user | The distinguished name or user ID used to bind. Previously entered DNs could be selected from drop-down list. |
| Bind Password | The password used to bind. |
| Save password | If checked the password will be saved in configuration. If not checked you have to enter the password whenever you connect to the server. Warning: The password is saved as plain text! |
| Check Authentication | Use this function if you want to attempt a connection plus a bind to the host upon completion of the wizard to validate that the entered information is correct. |
Additional authentication parameters for SASL and Kerberos:
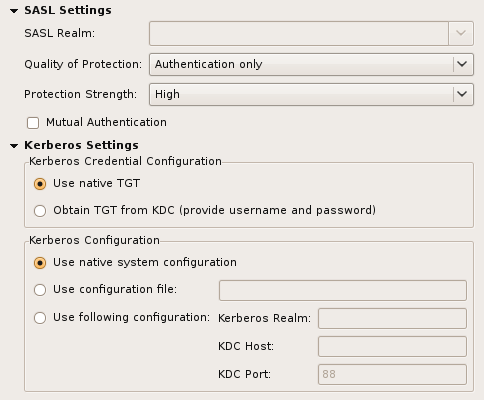
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| SASL Realm | The SASL Relam used to bind, only applicaple if DIGEST-MD5 is choosen. |
| Quality of Protection | The QoP to use: authentication only, with integrity protection, and with privacy protection |
| Protection Strength | The protection strength to use |
| Mutual Authentication | If checked mutual authentication is used, that means the server has to authenticate itself to the client. If unchecked only the client authenticates itself to the server. |
| Use native TGT | If checked the native credential cache is used, thus no additional authentication is necessary. Note that on Windows systems that requires a modification of the registry. |
| Object TGT from KDC | If checked a new TGT is obtained from the KDC. Username and password must be provided. |
| Use native system configuration | If checked the native Kerberos configuration is used (e.g. /etc/krb5.conf). |
| Use configuration file | If checked a custom configuration file could be used. |
| Use following configuration | If checked the Kerberos configuration parameters (realm, host, port) could be set in the dialog. |
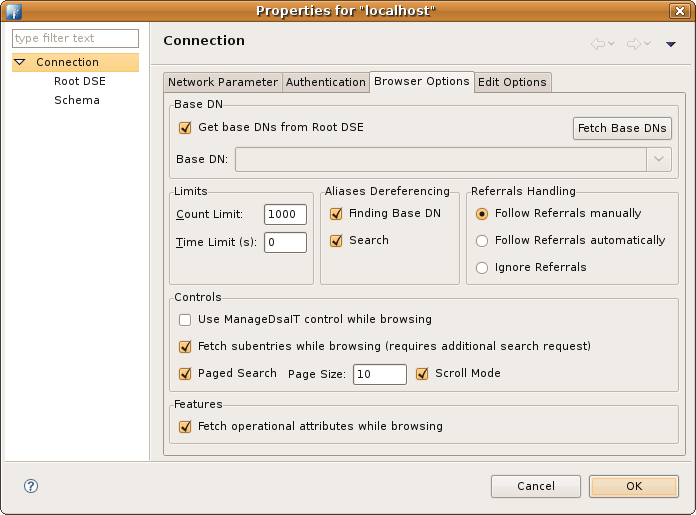
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Get base DNs from Root DSE | If checked the base DNs are fetched from namingContexts attribute of the Root DSE. |
| Fetch Base DNs | Use this function to get the namingContext values from the Root DSE. The returned values will appear in the 'Base DN' drop-down list. |
| Base DN | The base DN to use. You may enter a DN manually or you may select one from the drop-down list. This field is only enabled if the option 'Get base DNs from root DSE' is off. |
| Count Limit | Maximum number of entries returned from server when browsing the directory, it is also used as default value when searching the directory. A value of 0 means no count limit. Note that this value is a client-side value, its possible that also a server-side limit is used. |
| Time Limit | The maximum time in seconds the server searches for results. This is used as default value when browsing or searching the directory. A value of 0 means no limit. Note that this value is a client-side value, its possible that also a server-side limit is used. |
| Alias Dereferencing | Specifies whether aliases should be dereferenced while finding the search base entry or when performing the search or both. To manage (create, modify, delete) alias objects you have to uncheck both options. |
| Referrals Handling |
Specifies the referral handling.
|
| Use ManageDsaIT control while browsing | If enabled the ManageDsaIT control is sent to the server in each request. This signals the directory server to not send referrals and search continuations, but return the special referral objects. This only works if the directory server supports the ManageDsaIT control. |
| Fetch subentries while browsing | If enabled enabled both, normal and subentries according to RFC 3672 are fetched. This causes additional search requests while browsing the directory. |
| Paged Search | If enabled the simple paged result control is used while browsing the directory. With the page size you could define how many entries should be retrieved in one request. If Scroll Mode is enabled only one page is fetched from the server at once while browsing, you could 'scroll' through the pages by using the 'next page' and 'top page' items. If disabled all entries are fetched from the server, the paged result control is only used in background to avoid server-side limits. |
| Fetch operational attributes while browsing | If enabled enabled both, user attributes and operational attributes are retrieved while browsing. If the server supports the feature 'All Operational Attributes' then a '+' is used to retrieve operational attributes, otherwise all operational attributes defined in the schema are requested. |

| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Modify Mode |
Specify the modify mode for attributes with an equality matching rule.
Description of options:
|
| Modify Mode (no equality matching rule) |
Specify the modify mode for attributes with *no* equality matching rule.
Description of options:
|
| Modify Order | Specify the modify order when using add and delete operations. |
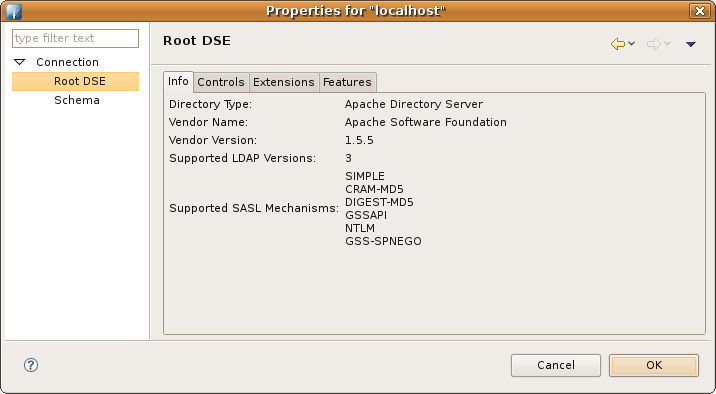
The Root DSE properties page provides information about the connected directory server like directory type and version, controls, extensions and features.

The Schema properties page provides some information about the schema. The 'Schema Information' group shows the schema DN an modification timestamp. With the 'Reload Schema' button a schema reload could be forced, the schema is reloaded automatically if the directory's schema is newer than the cached one. The 'Schema Cache' group shows information about the cached schema.