Building a Streaming ETL with Flink CDC #
This tutorial is to show how to quickly build streaming ETL for MySQL and Postgres with Flink CDC.
Assuming we are running an e-commerce business. The product and order data stored in MySQL, the shipment data related to the order is stored in Postgres. We want to enrich the orders using the product and shipment table, and then load the enriched orders to ElasticSearch in real time.
In the following sections, we will describe how to use Flink Mysql/Postgres CDC to implement it. All exercises in this tutorial are performed in the Flink SQL CLI, and the entire process uses standard SQL syntax, without a single line of Java/Scala code or IDE installation.
The overview of the architecture is as follows:

Preparation #
Prepare a Linux or MacOS computer with Docker installed.
Starting components required #
The components required in this demo are all managed in containers, so we will use docker-compose to start them.
Create docker-compose.yml file using following contents:
version: '2.1'
services:
postgres:
image: debezium/example-postgres:1.1
ports:
- "5432:5432"
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB=postgres
- POSTGRES_USER=postgres
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres
mysql:
image: debezium/example-mysql:1.1
ports:
- "3306:3306"
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456
- MYSQL_USER=mysqluser
- MYSQL_PASSWORD=mysqlpw
elasticsearch:
image: elastic/elasticsearch:7.6.0
environment:
- cluster.name=docker-cluster
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
- discovery.type=single-node
ports:
- "9200:9200"
- "9300:9300"
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
nofile:
soft: 65536
hard: 65536
kibana:
image: elastic/kibana:7.6.0
ports:
- "5601:5601"
The Docker Compose environment consists of the following containers:
- MySQL: the
products,orderstables will be store in the database. They will be joined with data in Postgres to enrich the orders. - Postgres: the
shipmentstable will be store in the database. - Elasticsearch: mainly used as a data sink to store enriched orders.
- Kibana: used to visualize the data in Elasticsearch.
To start all containers, run the following command in the directory that contains the docker-compose.yml file.
docker-compose up -d
This command automatically starts all the containers defined in the Docker Compose configuration in a detached mode. Run docker ps to check whether these containers are running properly. We can also visit http://localhost:5601/ to see if Kibana is running normally.
Preparing Flink and JAR package required #
-
Download Flink 1.18.0 and unzip it to the directory
flink-1.18.0 -
Download following JAR package required and put them under
flink-1.18.0/lib/:Download links are available only for stable releases, SNAPSHOT dependencies need to be built based on master or release branches by yourself.
- flink-sql-connector-elasticsearch7-3.0.1-1.17.jar
- flink-sql-connector-mysql-cdc-3.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
- flink-sql-connector-postgres-cdc-3.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
Preparing data in databases #
Preparing data in MySQL #
- Enter mysql’s container:
docker-compose exec mysql mysql -uroot -p123456 - Create tables and populate data:
-- MySQL CREATE DATABASE mydb; USE mydb; CREATE TABLE products ( id INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, description VARCHAR(512) ); ALTER TABLE products AUTO_INCREMENT = 101; INSERT INTO products VALUES (default,"scooter","Small 2-wheel scooter"), (default,"car battery","12V car battery"), (default,"12-pack drill bits","12-pack of drill bits with sizes ranging from #40 to #3"), (default,"hammer","12oz carpenter's hammer"), (default,"hammer","14oz carpenter's hammer"), (default,"hammer","16oz carpenter's hammer"), (default,"rocks","box of assorted rocks"), (default,"jacket","water resistent black wind breaker"), (default,"spare tire","24 inch spare tire"); CREATE TABLE orders ( order_id INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, order_date DATETIME NOT NULL, customer_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, price DECIMAL(10, 5) NOT NULL, product_id INTEGER NOT NULL, order_status BOOLEAN NOT NULL -- Whether order has been placed ) AUTO_INCREMENT = 10001; INSERT INTO orders VALUES (default, '2020-07-30 10:08:22', 'Jark', 50.50, 102, false), (default, '2020-07-30 10:11:09', 'Sally', 15.00, 105, false), (default, '2020-07-30 12:00:30', 'Edward', 25.25, 106, false);
Preparing data in Postgres #
- Enter postgres’s container:
docker-compose exec postgres psql -h localhost -U postgres - Create tables and populate data
-- PG CREATE TABLE shipments ( shipment_id SERIAL NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, order_id SERIAL NOT NULL, origin VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, destination VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, is_arrived BOOLEAN NOT NULL ); ALTER SEQUENCE public.shipments_shipment_id_seq RESTART WITH 1001; ALTER TABLE public.shipments REPLICA IDENTITY FULL; INSERT INTO shipments VALUES (default,10001,'Beijing','Shanghai',false), (default,10002,'Hangzhou','Shanghai',false), (default,10003,'Shanghai','Hangzhou',false);
Starting Flink cluster and Flink SQL CLI #
-
Use the following command to change to the Flink directory:
cd flink-1.18.0 -
Use the following command to start a Flink cluster:
./bin/start-cluster.shThen we can visit http://localhost:8081/ to see if Flink is running normally, and the web page looks like:
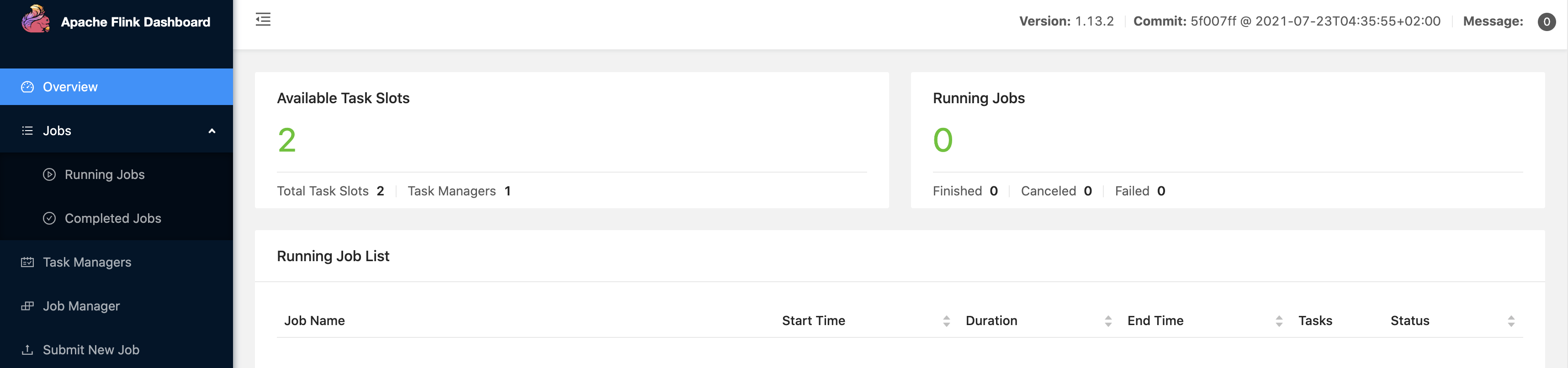
-
Use the following command to start a Flink SQL CLI:
./bin/sql-client.shWe should see the welcome screen of the CLI client.
Creating tables using Flink DDL in Flink SQL CLI #
First, enable checkpoints every 3 seconds
-- Flink SQL
Flink SQL> SET execution.checkpointing.interval = 3s;
Then, create tables that capture the change data from the corresponding database tables.
-- Flink SQL
Flink SQL> CREATE TABLE products (
id INT,
name STRING,
description STRING,
PRIMARY KEY (id) NOT ENFORCED
) WITH (
'connector' = 'mysql-cdc',
'hostname' = 'localhost',
'port' = '3306',
'username' = 'root',
'password' = '123456',
'database-name' = 'mydb',
'table-name' = 'products'
);
Flink SQL> CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id INT,
order_date TIMESTAMP(0),
customer_name STRING,
price DECIMAL(10, 5),
product_id INT,
order_status BOOLEAN,
PRIMARY KEY (order_id) NOT ENFORCED
) WITH (
'connector' = 'mysql-cdc',
'hostname' = 'localhost',
'port' = '3306',
'username' = 'root',
'password' = '123456',
'database-name' = 'mydb',
'table-name' = 'orders'
);
Flink SQL> CREATE TABLE shipments (
shipment_id INT,
order_id INT,
origin STRING,
destination STRING,
is_arrived BOOLEAN,
PRIMARY KEY (shipment_id) NOT ENFORCED
) WITH (
'connector' = 'postgres-cdc',
'hostname' = 'localhost',
'port' = '5432',
'username' = 'postgres',
'password' = 'postgres',
'database-name' = 'postgres',
'schema-name' = 'public',
'table-name' = 'shipments',
'slot.name' = 'flink'
);
Finally, create enriched_orders table that is used to load data to the Elasticsearch.
-- Flink SQL
Flink SQL> CREATE TABLE enriched_orders (
order_id INT,
order_date TIMESTAMP(0),
customer_name STRING,
price DECIMAL(10, 5),
product_id INT,
order_status BOOLEAN,
product_name STRING,
product_description STRING,
shipment_id INT,
origin STRING,
destination STRING,
is_arrived BOOLEAN,
PRIMARY KEY (order_id) NOT ENFORCED
) WITH (
'connector' = 'elasticsearch-7',
'hosts' = 'http://localhost:9200',
'index' = 'enriched_orders'
);
Enriching orders and load to ElasticSearch #
Use Flink SQL to join the order table with the products and shipments table to enrich orders and write to the Elasticsearch.
-- Flink SQL
Flink SQL> INSERT INTO enriched_orders
SELECT o.*, p.name, p.description, s.shipment_id, s.origin, s.destination, s.is_arrived
FROM orders AS o
LEFT JOIN products AS p ON o.product_id = p.id
LEFT JOIN shipments AS s ON o.order_id = s.order_id;
Now, the enriched orders should be shown in Kibana.
Visit http://localhost:5601/app/kibana#/management/kibana/index_pattern to create an index pattern enriched_orders.

Visit http://localhost:5601/app/kibana#/discover to find the enriched orders.

Next, do some change in the databases, and then the enriched orders shown in Kibana will be updated after each step in real time.
- Insert a new order in MySQL
--MySQL INSERT INTO orders VALUES (default, '2020-07-30 15:22:00', 'Jark', 29.71, 104, false); - Insert a shipment in Postgres
--PG INSERT INTO shipments VALUES (default,10004,'Shanghai','Beijing',false); - Update the order status in MySQL
--MySQL UPDATE orders SET order_status = true WHERE order_id = 10004; - Update the shipment status in Postgres
--PG UPDATE shipments SET is_arrived = true WHERE shipment_id = 1004; - Delete the order in MySQL
The changes of enriched orders in Kibana are as follows:
--MySQL DELETE FROM orders WHERE order_id = 10004;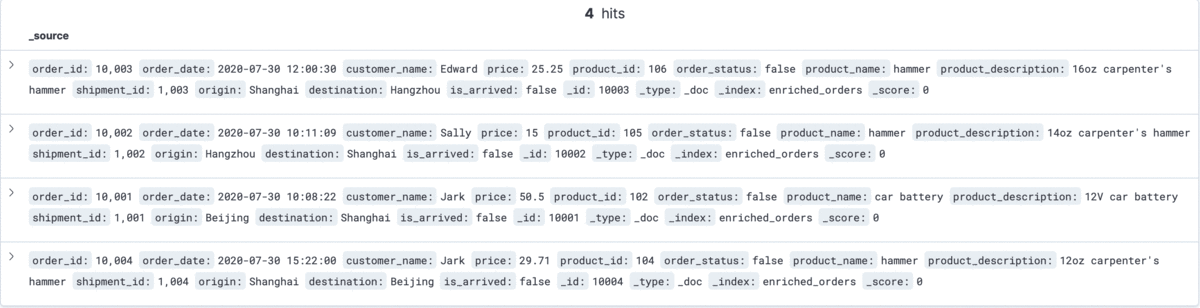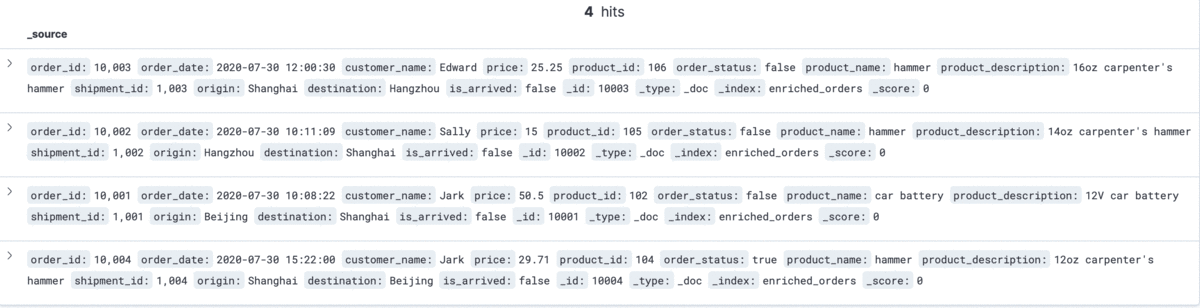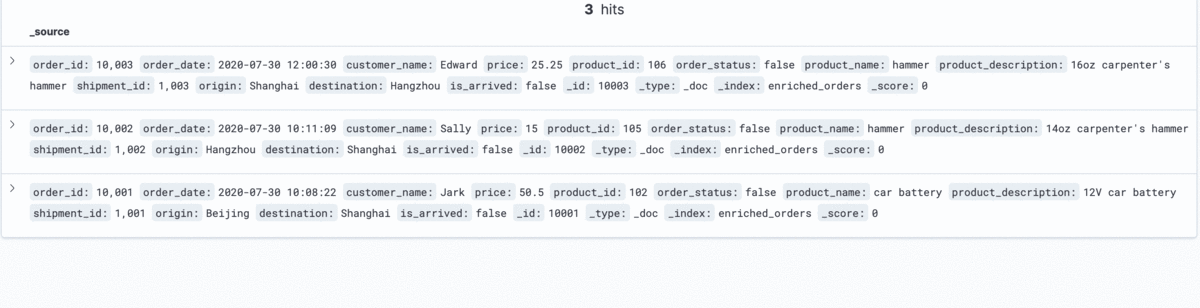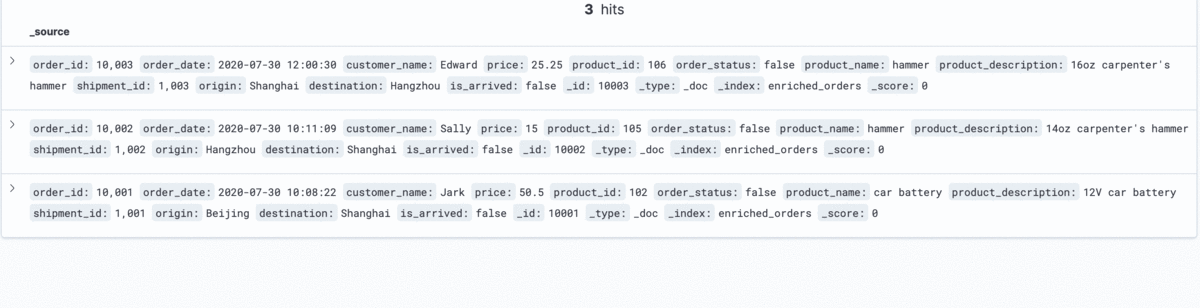
Clean up #
After finishing the tutorial, run the following command to stop all containers in the directory of docker-compose.yml:
docker-compose down
Run the following command to stop the Flink cluster in the directory of Flink flink-1.18.0:
./bin/stop-cluster.sh


