Quickstart: Setup
Get a Flink example program up and running in a few simple steps.
Setup: Download and Start
Flink runs on Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows. To be able to run Flink, the only requirement is to have a working Java 7.x (or higher) installation. Windows users, please take a look at the Flink on Windows guide which describes how to run Flink on Windows for local setups.
Download
Download a binary from the downloads page. You can pick any Hadoop/Scala combination you like.
Start a Local Flink Cluster
- Go to the download directory.
- Unpack the downloaded archive.
- Start Flink.
$ cd ~/Downloads # Go to download directory
$ tar xzf flink-*.tgz # Unpack the downloaded archive
$ cd flink-1.1.5
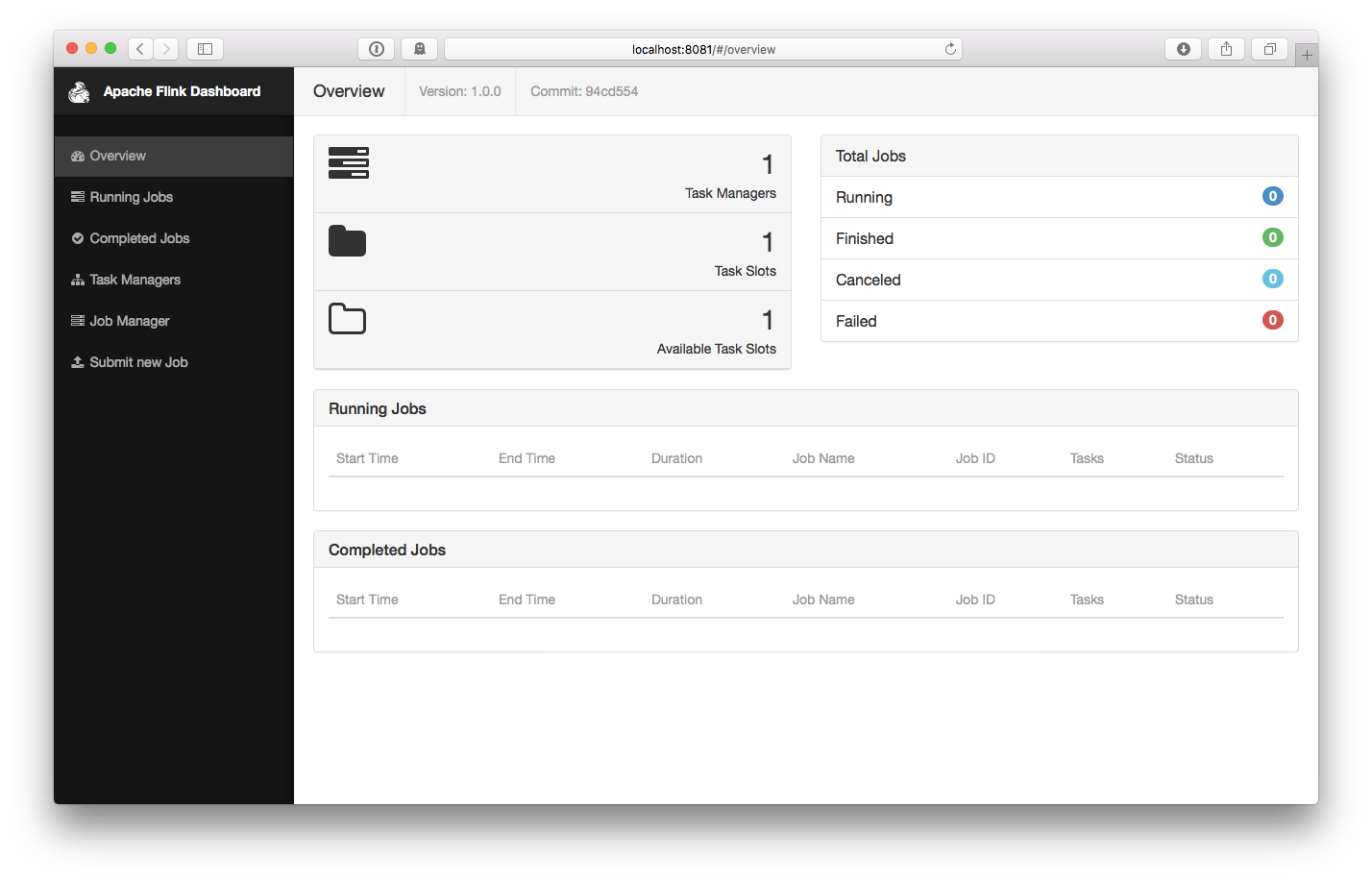
$ bin/start-local.sh # Start FlinkCheck the JobManager’s web frontend at http://localhost:8081 and make sure everything is up and running. The web frontend should report a single available TaskManager instance.
Run Example
Now, we are going to run the SocketWindowWordCount example and read text from a socket and count the number of distinct words.
-
First of all, we use netcat to start local server via
$ nc -l 9000 -
Submit the Flink program:
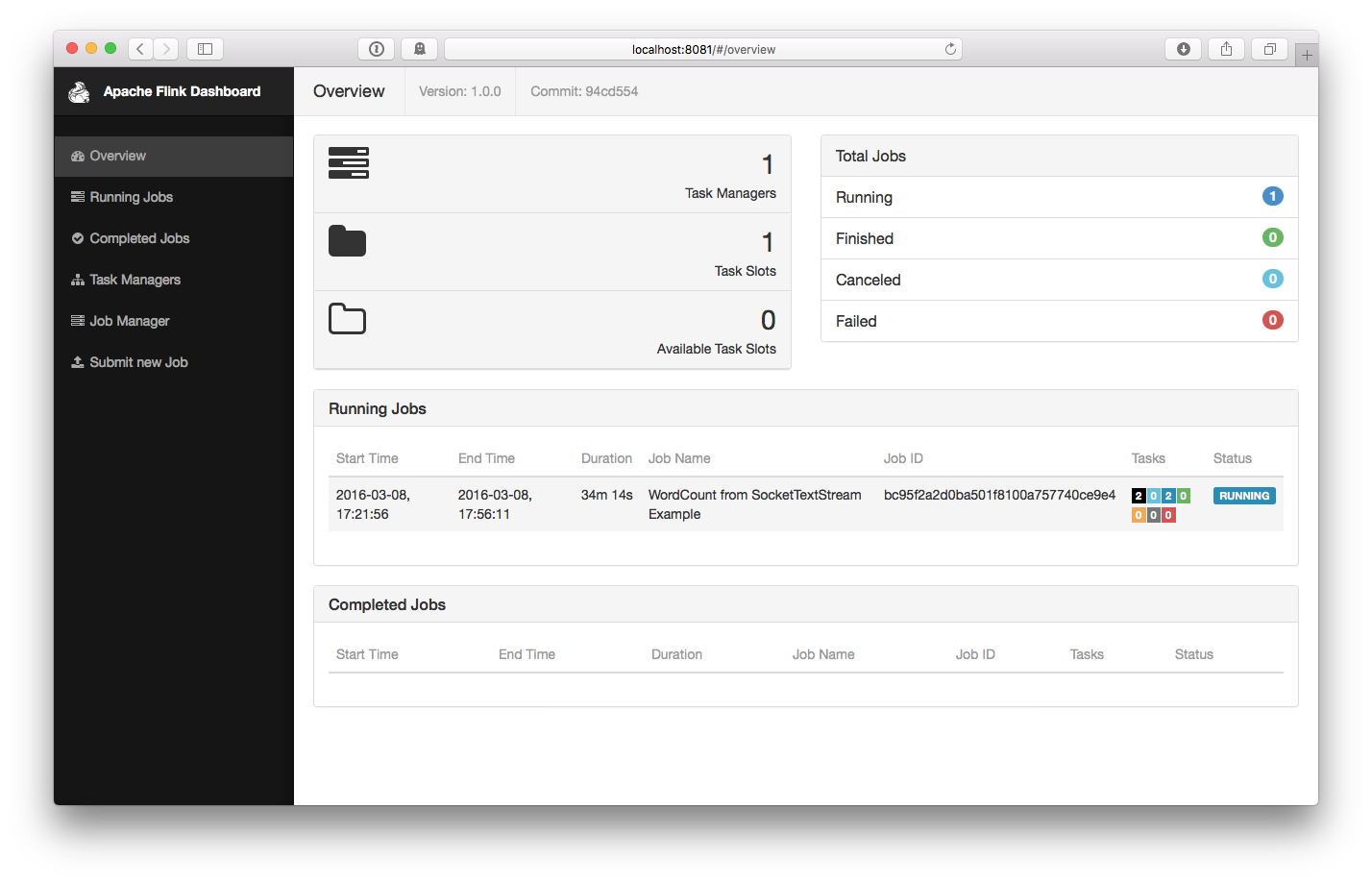
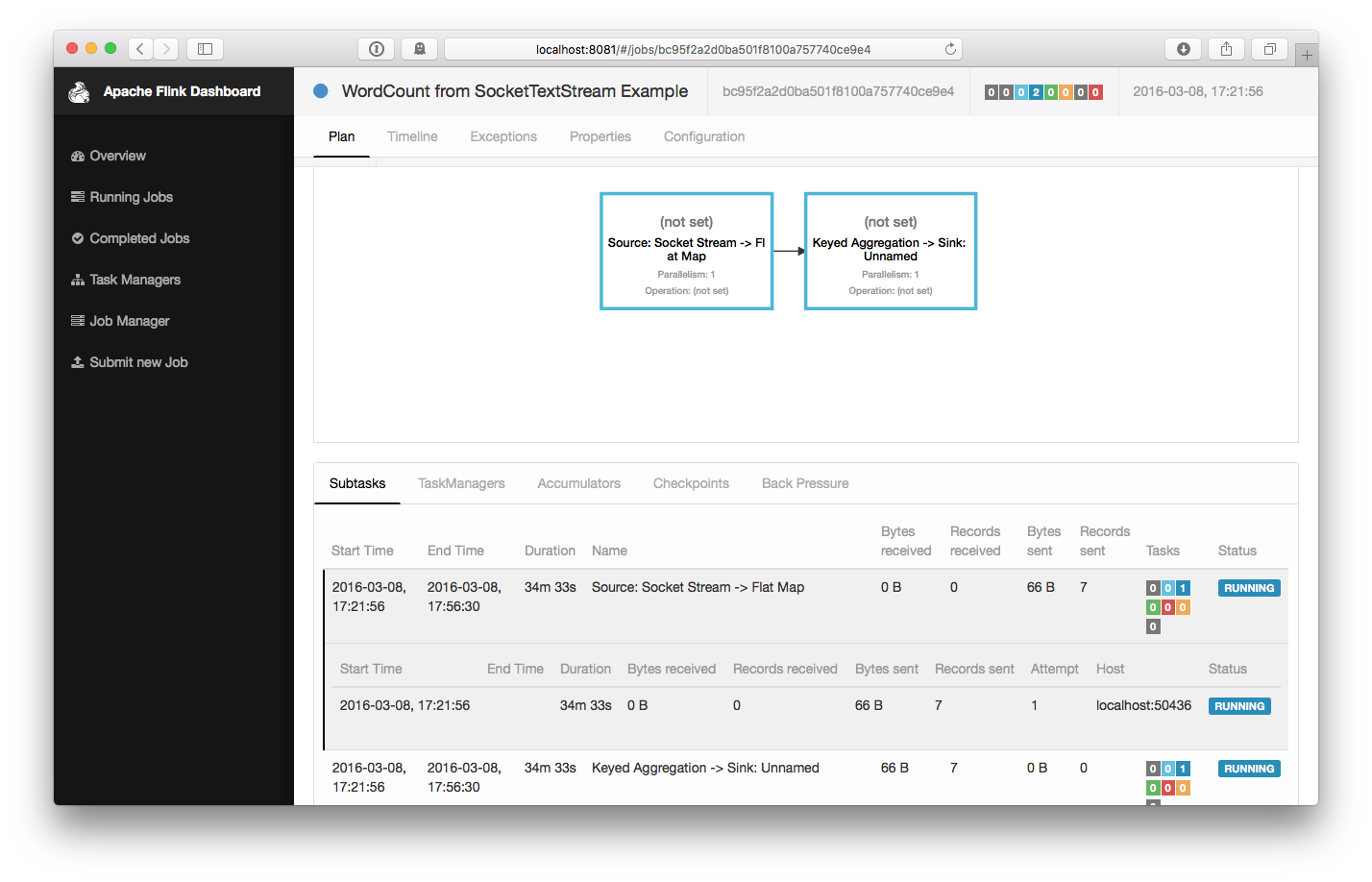
$ bin/flink run examples/streaming/SocketWindowWordCount.jar --port 9000 03/08/2016 17:21:56 Job execution switched to status RUNNING. 03/08/2016 17:21:56 Source: Socket Stream -> Flat Map(1/1) switched to SCHEDULED 03/08/2016 17:21:56 Source: Socket Stream -> Flat Map(1/1) switched to DEPLOYING 03/08/2016 17:21:56 Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Unnamed(1/1) switched to SCHEDULED 03/08/2016 17:21:56 Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Unnamed(1/1) switched to DEPLOYING 03/08/2016 17:21:56 Source: Socket Stream -> Flat Map(1/1) switched to RUNNING 03/08/2016 17:21:56 Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Unnamed(1/1) switched to RUNNINGThe program connects to the socket and waits for input. You can check the web interface to verify that the job is running as expected:
-
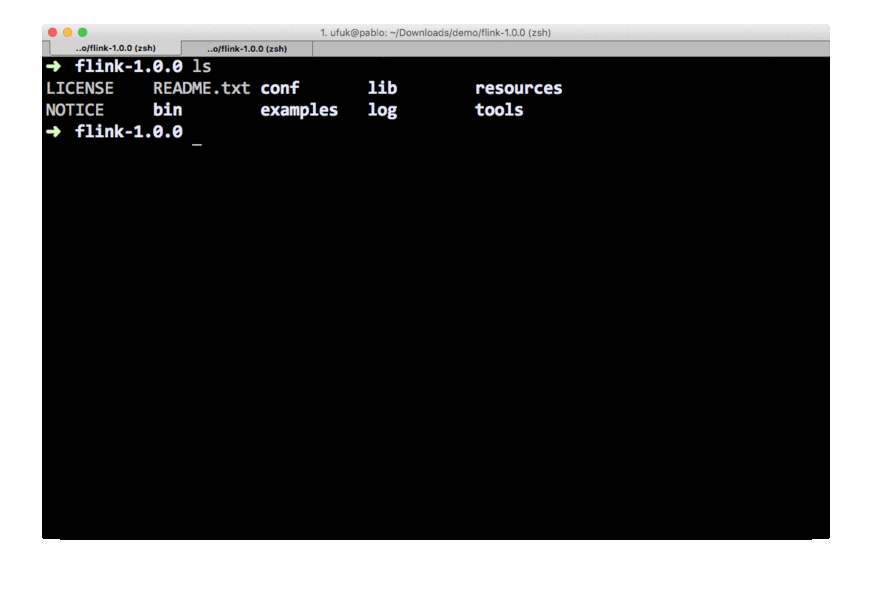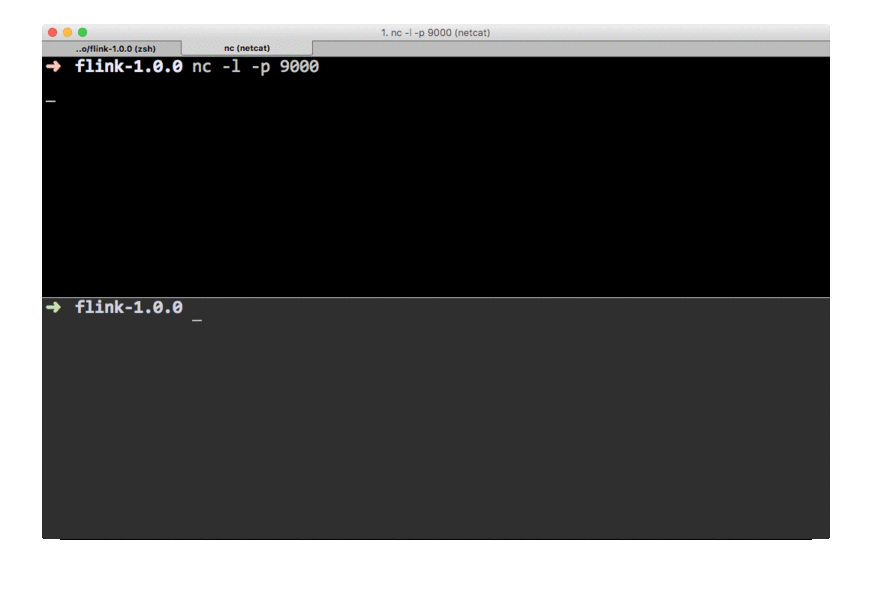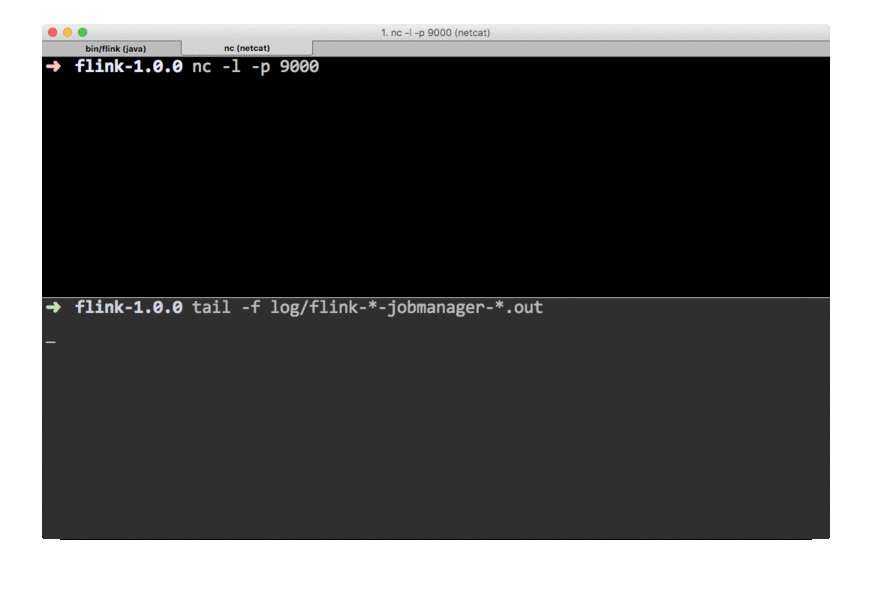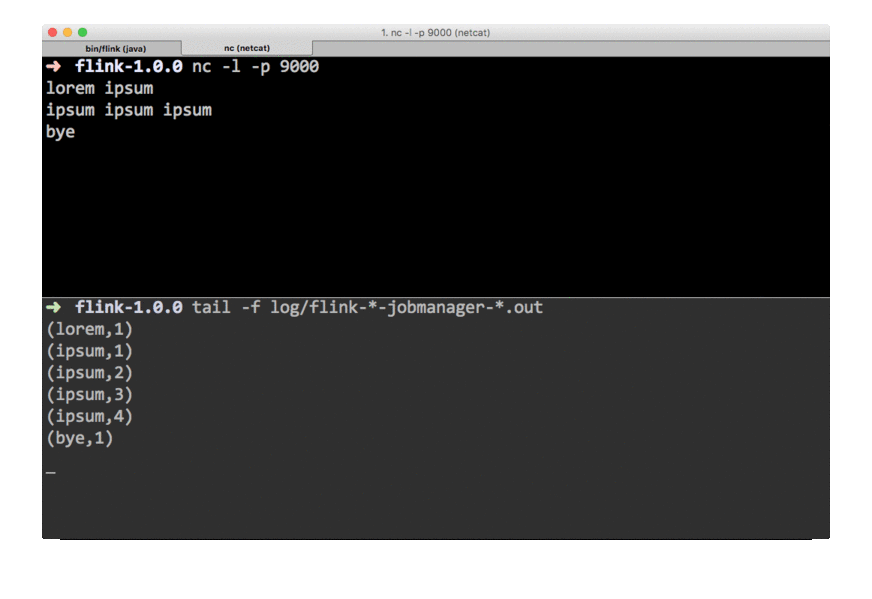
Counts are printed to
stdout. Monitor the JobManager’s output file and write some text innc:$ nc -l 9000 lorem ipsum ipsum ipsum ipsum byeThe
.outfile will print the counts immediately:$ tail -f log/flink-*-jobmanager-*.out (lorem,1) (ipsum,1) (ipsum,2) (ipsum,3) (ipsum,4) (bye,1)To stop Flink when you’re done type:
$ bin/stop-local.sh
Next Steps
Check out the step-by-step example in order to get a first feel of Flink’s programming APIs. When you are done with that, go ahead and read the streaming guide.
Cluster Setup
Running Flink on a cluster is as easy as running it locally. Having passwordless SSH and the same directory structure on all your cluster nodes lets you use our scripts to control everything.
- Copy the unpacked flink directory from the downloaded archive to the same file system path on each node of your setup.
- Choose a master node (JobManager) and set the
jobmanager.rpc.addresskey inconf/flink-conf.yamlto its IP or hostname. Make sure that all nodes in your cluster have the samejobmanager.rpc.addressconfigured. - Add the IPs or hostnames (one per line) of all worker nodes (TaskManager) to the slaves files
in
conf/slaves.
You can now start the cluster at your master node with bin/start-cluster.sh.
The following example illustrates the setup with three nodes (with IP addresses from 10.0.0.1 to 10.0.0.3 and hostnames master, worker1, worker2) and shows the contents of the configuration files, which need to be accessible at the same path on all machines:
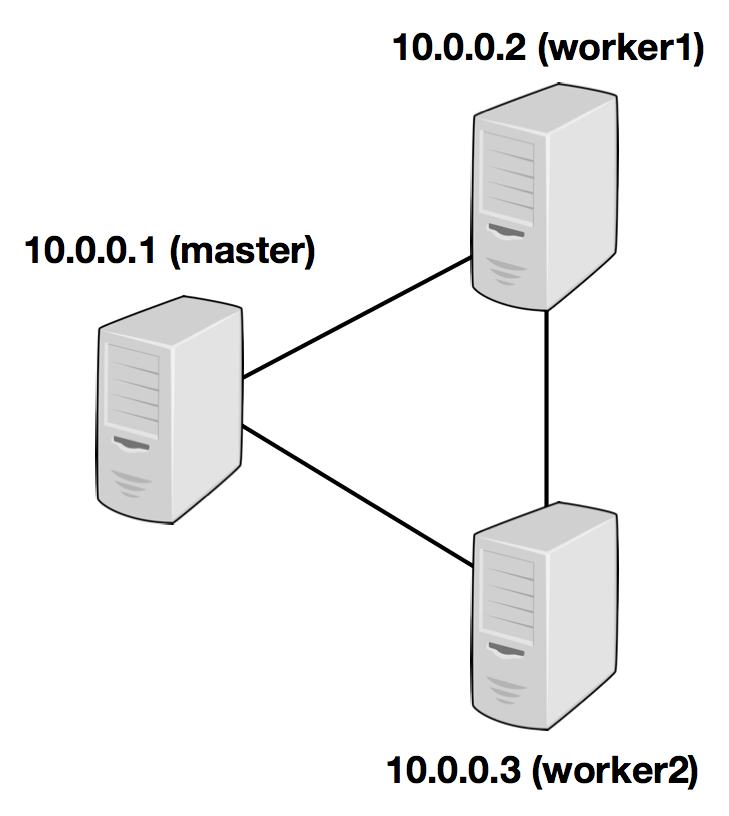
/path/to/flink/conf/
flink-conf.yaml
jobmanager.rpc.address: 10.0.0.1
/path/to/flink/
conf/slaves
10.0.0.2 10.0.0.3
Have a look at the Configuration section of the documentation to see other available configuration options. For Flink to run efficiently, a few configuration values need to be set.
In particular,
- the amount of available memory per TaskManager (
taskmanager.heap.mb), - the number of available CPUs per machine (
taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots), - the total number of CPUs in the cluster (
parallelism.default) and - the temporary directories (
taskmanager.tmp.dirs)
are very important configuration values.
Flink on YARN
You can easily deploy Flink on your existing YARN cluster.
- Download the Flink Hadoop2 package from the downloads page
- Make sure your HADOOP_HOME (or YARN_CONF_DIR or HADOOP_CONF_DIR) environment variable is set to read your YARN and HDFS configuration.
- Run the YARN client with:
./bin/yarn-session.sh. You can run the client with options-n 10 -tm 8192to allocate 10 TaskManagers with 8GB of memory each.