Monitoring Checkpointing
Overview
Flink’s web interface provides a tab to monitor the checkpoints of jobs. These stats are also available after the job has terminated. There are four different tabs to display information about your checkpoints: Overview, History, Summary, and Configuration. The following sections will cover all of these in turn.
Monitoring
Overview Tab
The overview tabs lists the following statistics. Note that these statistics don’t survive a JobManager loss and are reset to if your JobManager fails over.
- Checkpoint Counts
- Triggered: The total number of checkpoints that have been triggered since the job started.
- In Progress: The current number of checkpoints that are in progress.
- Completed: The total number of successfully completed checkpoints since the job started.
- Failed: The total number of failed checkpoints since the job started.
- Restored: The number of restore operations since the job started. This also tells you how many times the job has restarted since submission. Note that the initial submission with a savepoint also counts as a restore and the count is reset if the JobManager was lost during operation.
- Latest Completed Checkpoint: The latest successfully completed checkpoints. Clicking on
More detailsgives you detailed statistics down to the subtask level. - Latest Failed Checkpoint: The latest failed checkpoint. Clicking on
More detailsgives you detailed statistics down to the subtask level. - Latest Savepoint: The latest triggered savepoint with its external path. Clicking on
More detailsgives you detailed statistics down to the subtask level. - Latest Restore: There are two types of restore operations.
- Restore from Checkpoint: We restored from a regular periodic checkpoint.
- Restore from Savepoint: We restored from a savepoint.
History Tab
The checkpoint history keeps statistics about recently triggered checkpoints, including those that are currently in progress.
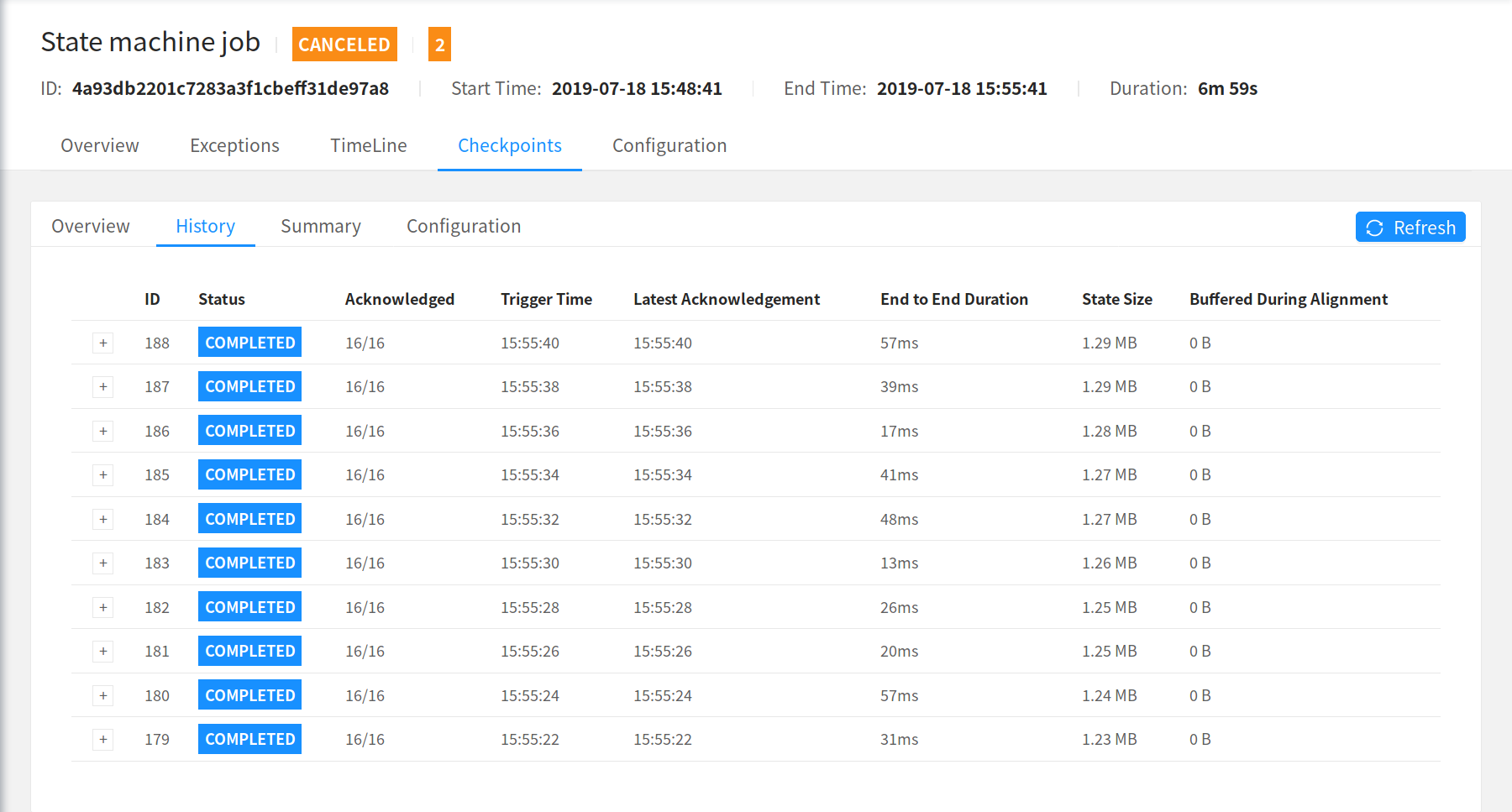
- ID: The ID of the triggered checkpoint. The IDs are incremented for each checkpoint, starting at 1.
- Status: The current status of the checkpoint, which is either In Progress (), Completed (), or Failed (). If the triggered checkpoint is a savepoint, you will see a symbol.
- Trigger Time: The time when the checkpoint was triggered at the JobManager.
- Latest Acknowledgement: The time when the latest acknowledged for any subtask was received at the JobManager (or n/a if no acknowledgement received yet).
- End to End Duration: The duration from the trigger timestamp until the latest acknowledgement (or n/a if no acknowledgement received yet). This end to end duration for a complete checkpoint is determined by the last subtask that acknowledges the checkpoint. This time is usually larger than single subtasks need to actually checkpoint the state.
- State Size: The state size over all acknowledged subtasks.
- Buffered During Alignment: The number of bytes buffered during alignment over all acknowledged subtasks. This is only > 0 if a stream alignment takes place during checkpointing. If the checkpointing mode is
AT_LEAST_ONCEthis will always be zero as at least once mode does not require stream alignment.
History Size Configuration
You can configure the number of recent checkpoints that are remembered for the history via the following configuration key. The default is 10.
# Number of recent checkpoints that are remembered
web.checkpoints.history: 15Summary Tab
The summary computes a simple min/average/maximum statistics over all completed checkpoints for the End to End Duration, State Size, and Bytes Buffered During Alignment (see History for details about what these mean).
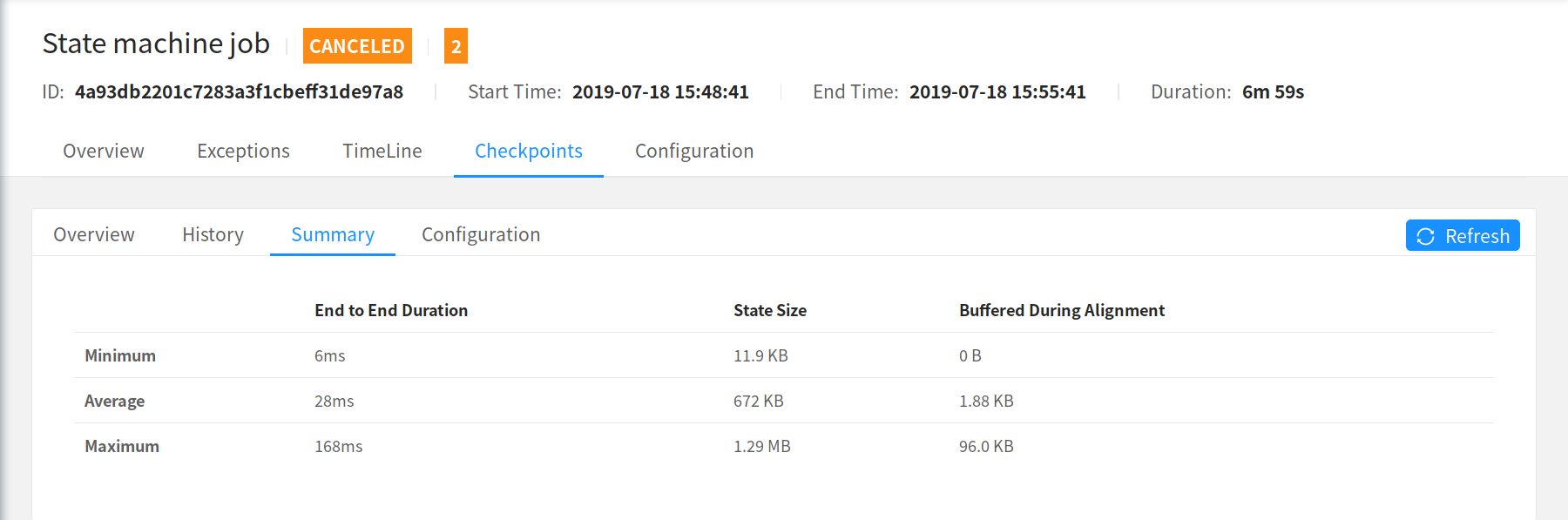
Note that these statistics don’t survive a JobManager loss and are reset to if your JobManager fails over.
Configuration Tab
The configuration list your streaming configuration:
- Checkpointing Mode: Either Exactly Once or At least Once.
- Interval: The configured checkpointing interval. Trigger checkpoints in this interval.
- Timeout: Timeout after which a checkpoint is cancelled by the JobManager and a new checkpoint is triggered.
- Minimum Pause Between Checkpoints: Minimum required pause between checkpoints. After a checkpoint has completed successfully, we wait at least for this amount of time before triggering the next one, potentially delaying the regular interval.
- Maximum Concurrent Checkpoints: The maximum number of checkpoints that can be in progress concurrently.
- Persist Checkpoints Externally: Enabled or Disabled. If enabled, furthermore lists the cleanup config for externalized checkpoints (delete or retain on cancellation).
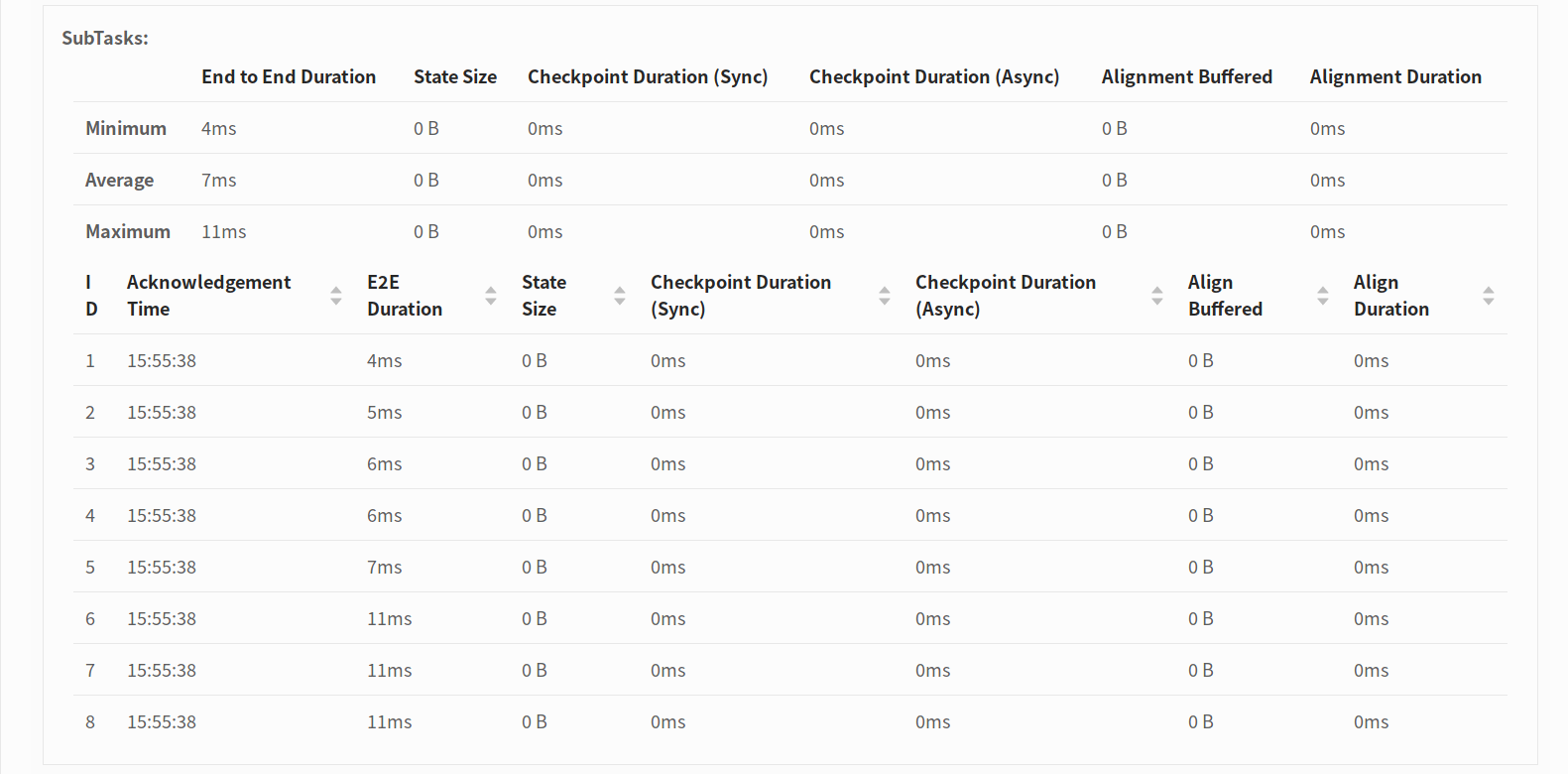
Checkpoint Details
When you click on a More details link for a checkpoint, you get a Minimum/Average/Maximum summary over all its operators and also the detailed numbers per single subtask.
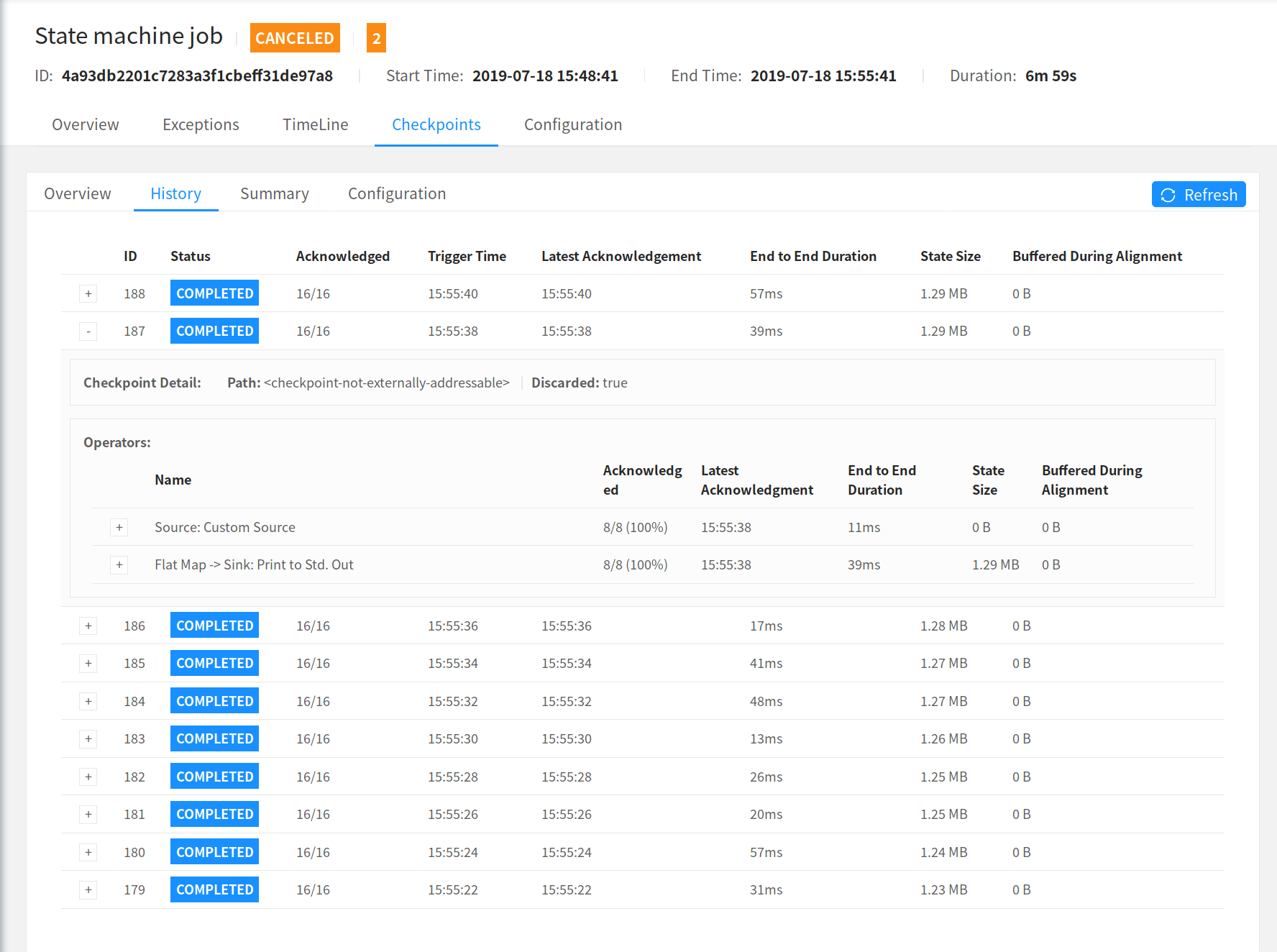
Summary per Operator
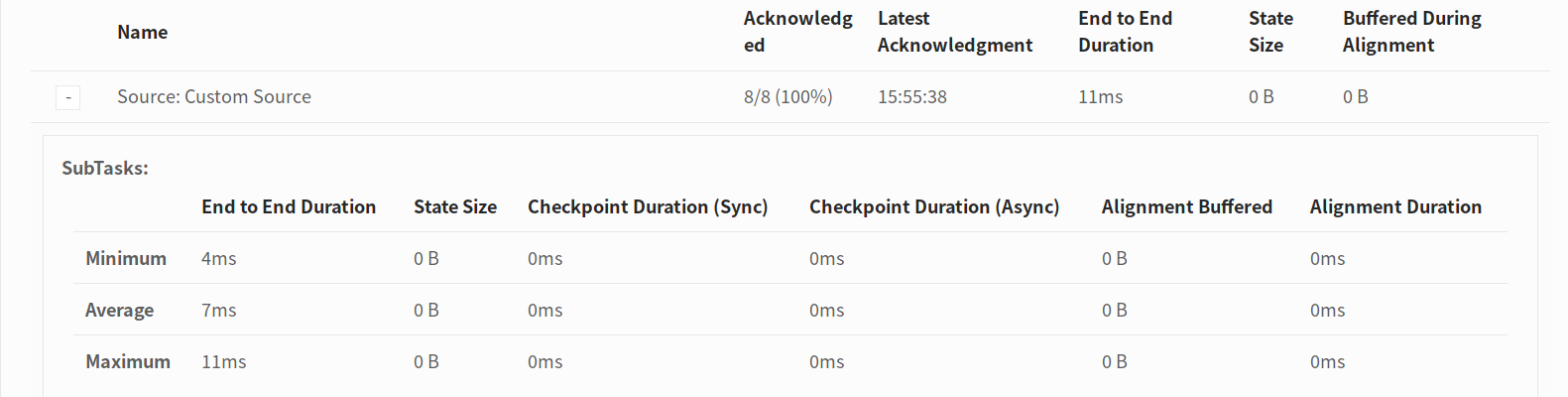
All Subtask Statistics