This documentation is for an unreleased version of Apache Flink. We recommend you use the latest stable version.
State Processor API #
Apache Flink 的 State Processor API 提供了批模式 (BATCH) 下使用 DataStream API 读取、写入、修改 savepoint 和 checkpoint 的强大能力。 由于 DataStream 和 Table API 是等价的,也可以使用 Table API 或 SQL 来分析和处理 savepoint 或 checkpoint 中的状态数据。
例如,可以获取一个正在运行的流应用程序的 savepoint,使用 State Processor API 在批模式下对该 savepoint 进行分析,以验证应用程序的行为是否正确; 还可以从任意存储中读取并预处理一批数据后将结果写入一个 savepoint,然后基于这个 savepoint 初始化流应用程序的状态; State Processor API 也可以用来修复不一致的状态条目。 State Processor API 为有状态应用程序的演化提供了新的方式。以前有状态应用程序不能够进行更改,否则会丢失所有状态。现在可以通过 State Processor API 修改状态的数据类型、调整操作符的最大并行度、拆分或合并操作符状态、重新分配操作符 UID 等。
请在应用程序中包含以下库以使用 State Processor API。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-state-processor-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>从状态到数据集 #
State Processor API 将流应用程序的状态映射到若干个可以单独处理的数据集中,为了能使用 API,您需要先理解这种映射是如何工作的。
让我们先看看有状态的 Flink 作业是什么样子的。Flink 作业由算子 (Operator) 组成: 一个作业通常包括若干个 Source 算子,一些实际用于计算处理的算子以及若干个 Sink 算子。 每个算子由若干个子任务并行运行,一个算子中可以有不同类型的 State。一个算子可以有若干个 operator state,这些状态被组织成列表,每个子任务的 State 对应列表中的一个元素。 如果一个算子是 keyed stream 中的,则它可以有若干个 keyed state,用来存储从 record 中提取出的 key,keyed state 可以看作分布式键值映射。
下图展示了应用程序 MyApp 中的状态,它由三个名为 Src、Proc 和 Snk 的算子组成。Src 算子有一个 operator state (os1),Proc 算子有一个 operator state (os2) 和两个 keyed state (ks1、ks2),Snk 算子是无状态的。
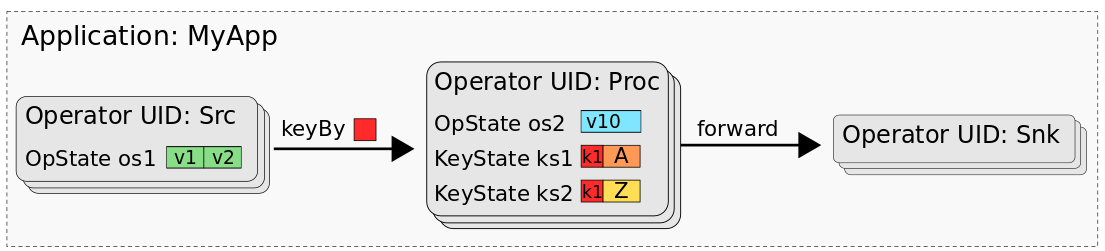
MyApp 的 savepoint 或 checkpoint 包含了所有状态数据,可以用来恢复每个子任务的状态。当使用批处理作业处理 savepoint/checkpoint 的数据时,我们需要一个映射模型,将各个任务的状态数据映射到数据集中。 事实上,可以将 savepoint 视为数据库,每个算子(由其 UID 标识)代表一个命名空间。算子的 operator state 可以映射为命名空间中一个单列的表,表中的一行代表一个子任务。 算子所有的 keyed state 可以看作一个多列的表,每一列表示一个 keyed state。下图展示了 MyApp 的 savepoint 和数据集间的映射关系。
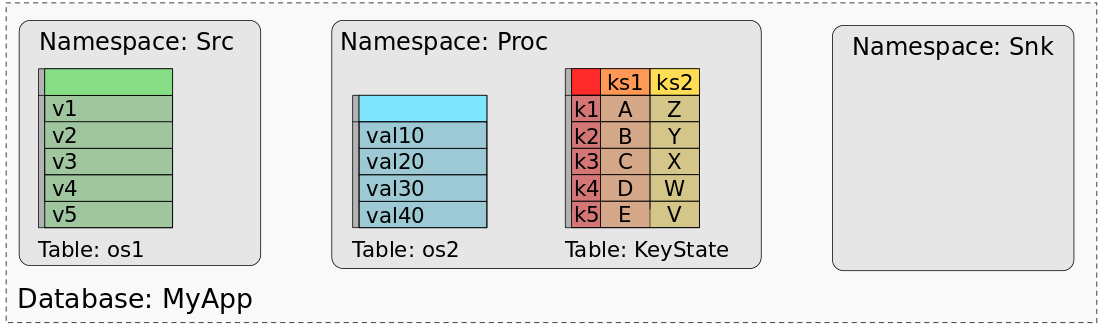
上图显示了 Src 算子的 operator state 与数据集的映射,数据集的每一行表示一个 Src 算子的子任务的状态。 Proc 算子的 os2 也类似地映射到一个单列的表。Proc 算子的 ks1 和 ks2 组合成一个三列的表,第一列表示key,第二列表示 ks1,第三列表示 ks2,每一行表示一个 key 的状态。 Snk 算子没有状态,因此它的命名空间是空的。
算子的标识 #
State Processor API 允许使用 UIDs 或 UID hash来识别算子:OperatorIdentifier#forUid/forUidHash。
仅当无法使用 UID 时才应使用 UID hash,例如,当创建 savepoint 的应用程序未指定 UID 或算子 UID 未知时。
通过 State Processor API 读取状态 #
读取状态首先需要指定 savepoint 或 checkpoint 的路径以及用于恢复数据的 状态存储后端 (StateBackend)。State processor API 恢复的状态与 DataStream 应用恢复的状态是一致的。
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
SavepointReader savepoint = SavepointReader.read(env, "hdfs://path/", new HashMapStateBackend());
Operator State #
Flink 中的 non-keyed state 被称为 operator state。
在应用程序中使用 CheckpointedFunction 或 BroadcastState 会生成 operator State。 读取 operator state 时,需要指定算子 UID、状态名称和类型信息。
Operator List State #
通过 getListState 存储在 CheckpointedFunction 中的 operator state 可以用 SavepointReader#readListState 读取。
状态名称和类型信息应该与定义在 DataStream 应用程序中声明此状态的 ListStateDescriptor 相匹配。
DataStream<Integer> listState = savepoint.readListState<>(
OperatorIdentifier.forUid("my-uid"),
"list-state",
Types.INT);
Operator Union List State #
通过 getUnionListState 存储在 CheckpointedFunction 中的 operator state 可以用 SavepointReader#readUnionState 读取。
状态名称和类型信息应该与定义在 DataStream 应用程序中声明此状态的 ListStateDescriptor 相匹配。
State Processor API 将返回一个状态的 单 副本,可以看作并发度为 1 的 DataStream 应用。
DataStream<Integer> listState = savepoint.readUnionState<>(
OperatorIdentifier.forUid("my-uid"),
"union-state",
Types.INT);
广播状态 Broadcast State #
可以用 SavepointReader#readBroadcastState 读取 BroadcastState。
状态名称和类型信息应该与定义在 DataStream 应用程序中声明此状态的 MapStateDescriptor 相匹配。
State Processor API 将返回一个状态的 单 副本,可以看作并发度为 1 的 DataStream 应用。
DataStream<Tuple2<Integer, Integer>> broadcastState = savepoint.readBroadcastState<>(
OperatorIdentifier.forUid("my-uid"),
"broadcast-state",
Types.INT,
Types.INT);
使用自定义序列化器 #
如果在写出状态时 StateDescriptor 使用了自定义的 TypeSerializer,Operator state 也支持使用自定义的 TypeSerializers 来读取。
DataStream<Integer> listState = savepoint.readListState<>(
OperatorIdentifier.forUid("uid"),
"list-state",
Types.INT,
new MyCustomIntSerializer());
Keyed State #
Keyed state,又叫分区状态 (partitioned state),是使用一个 key 进行分区的状态。
当读取 keyed state 时,需要指定算子 id 和一个 KeyedStateReaderFunction<KeyType, OutputType>。
KeyedStateReaderFunction 允许用户读取任意列和复杂的状态类型,如 ListState, MapState, 和 AggregatingState。
这意味着如果一个算子包含一个带状态的处理函数,如:
public class StatefulFunctionWithTime extends KeyedProcessFunction<Integer, Integer, Void> {
ValueState<Integer> state;
ListState<Long> updateTimes;
@Override
public void open(OpenContext openContext) {
ValueStateDescriptor<Integer> stateDescriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor<>("state", Types.INT);
state = getRuntimeContext().getState(stateDescriptor);
ListStateDescriptor<Long> updateDescriptor = new ListStateDescriptor<>("times", Types.LONG);
updateTimes = getRuntimeContext().getListState(updateDescriptor);
}
@Override
public void processElement(Integer value, Context ctx, Collector<Void> out) throws Exception {
state.update(value + 1);
updateTimes.add(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
算子中的状态可以通过定义输出类型和相应的 KeyedStateReaderFunction 来读取。
DataStream<KeyedState> keyedState = savepoint.readKeyedState(OperatorIdentifier.forUid("my-uid"), new ReaderFunction());
public class KeyedState {
public int key;
public int value;
public List<Long> times;
}
public class ReaderFunction extends KeyedStateReaderFunction<Integer, KeyedState> {
ValueState<Integer> state;
ListState<Long> updateTimes;
@Override
public void open(OpenContext openContext) {
ValueStateDescriptor<Integer> stateDescriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor<>("state", Types.INT);
state = getRuntimeContext().getState(stateDescriptor);
ListStateDescriptor<Long> updateDescriptor = new ListStateDescriptor<>("times", Types.LONG);
updateTimes = getRuntimeContext().getListState(updateDescriptor);
}
@Override
public void readKey(
Integer key,
Context ctx,
Collector<KeyedState> out) throws Exception {
KeyedState data = new KeyedState();
data.key = key;
data.value = state.value();
data.times = StreamSupport
.stream(updateTimes.get().spliterator(), false)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
out.collect(data);
}
}
除了读取注册的状态之外,每个 key 还可以访问包括 event time 和 processing time 计时器等元数据的 Context。
注意: 当使用 KeyedStateReaderFunction 时,所有状态描述符必须在 open 函数中注册。 否则任何尝试调用 RuntimeContext#get*State 将导致 RuntimeException。
窗口状态 Window State #
State Processor API 支持读取窗口算子的状态,当读取窗口状态时,需要指定算子 id,窗口分配器和聚合类型。
此外,可以指定类似于 WindowFunction 或 ProcessWindowFunction 的 WindowReaderFunction 来增强每次读取的附加信息。
假设下面是一个统计用户每分钟点击次数的 DataStream 应用程序。
class Click {
public String userId;
public LocalDateTime time;
}
class ClickCounter implements AggregateFunction<Click, Integer, Integer> {
@Override
public Integer createAccumulator() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Integer add(Click value, Integer accumulator) {
return 1 + accumulator;
}
@Override
public Integer getResult(Integer accumulator) {
return accumulator;
}
@Override
public Integer merge(Integer a, Integer b) {
return a + b;
}
}
DataStream<Click> clicks = ...;
clicks
.keyBy(click -> click.userId)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Duration.ofMinutes(1)))
.aggregate(new ClickCounter())
.uid("click-window")
.addSink(new Sink());
它的状态可以通过如下方式读取。
class ClickState {
public String userId;
public int count;
public TimeWindow window;
public Set<Long> triggerTimers;
}
class ClickReader extends WindowReaderFunction<Integer, ClickState, String, TimeWindow> {
@Override
public void readWindow(
String key,
Context<TimeWindow> context,
Iterable<Integer> elements,
Collector<ClickState> out) {
ClickState state = new ClickState();
state.userId = key;
state.count = elements.iterator().next();
state.window = context.window();
state.triggerTimers = context.registeredEventTimeTimers();
out.collect(state);
}
}
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
SavepointReader savepoint = SavepointReader.read(env, "hdfs://checkpoint-dir", new HashMapStateBackend());
savepoint
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Duration.ofMinutes(1)))
.aggregate("click-window", new ClickCounter(), new ClickReader(), Types.String, Types.INT, Types.INT)
.print();
另外,可以通过 WindowReaderFunction 里的 Context#triggerState 方法读取 CountTrigger 或自定义触发器的状态。
通过 State Processor API 生成新 savepoint #
State processor API 可以用来生成 savepoint,这使得用户可以基于历史数据进行状态的初始化。
每个 savepoint 可以由若干个 StateBootstrapTransformation 生成,每个 StateBootstrapTransformation 定义了一个算子的状态。
当使用 SavepointWriter 时,您的应用程序必须在 批 执行模式下运行。
注意 State processor API 目前不支持 Scala API。 因此它将自动使用 Java 类型的序列化器。 为了能让 Scala DataStream API 从 state processor API 生成的 savepoint 中启动,请手动传递所有类型信息。
int maxParallelism = 128;
SavepointWriter
.newSavepoint(env, new HashMapStateBackend(), maxParallelism)
.withOperator(OperatorIdentifier.forUid("uid1"), transformation1)
.withOperator(OperatorIdentifier.forUid("uid2"), transformation2)
.write(savepointPath);
与每个算子关联的 UID 必须与 DataStream 应用程序中分配给算子的 UID 一一对应;这样 Flink 才能知道什么状态映射到哪个算子。
Operator State #
Simple operator state, using CheckpointedFunction, can be created using the StateBootstrapFunction.
在 DataStream API 中通过 CheckpointedFunction 创建出的、简单的 operator state,在 state processor API 中可以用 StateBootstrapFunction 创建。
public class SimpleBootstrapFunction extends StateBootstrapFunction<Integer> {
private ListState<Integer> state;
@Override
public void processElement(Integer value, Context ctx) throws Exception {
state.add(value);
}
@Override
public void snapshotState(FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception {
}
@Override
public void initializeState(FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception {
state = context.getOperatorState().getListState(new ListStateDescriptor<>("state", Types.INT));
}
}
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Integer> data = env.fromElements(1, 2, 3);
StateBootstrapTransformation transformation = OperatorTransformation
.bootstrapWith(data)
.transform(new SimpleBootstrapFunction());
广播状态 Broadcast State #
BroadcastState 可以用 BroadcastStateBootstrapFunction 生成。与 DataStream API 中的 broadcast state 一样,它的全部状态必须能完全放入内存。
public class CurrencyRate {
public String currency;
public Double rate;
}
public class CurrencyBootstrapFunction extends BroadcastStateBootstrapFunction<CurrencyRate> {
public static final MapStateDescriptor<String, Double> descriptor =
new MapStateDescriptor<>("currency-rates", Types.STRING, Types.DOUBLE);
@Override
public void processElement(CurrencyRate value, Context ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.getBroadcastState(descriptor).put(value.currency, value.rate);
}
}
DataStream<CurrencyRate> currencyDataSet = env.fromCollection(
new CurrencyRate("USD", 1.0), new CurrencyRate("EUR", 1.3));
StateBootstrapTransformation<CurrencyRate> broadcastTransformation = OperatorTransformation
.bootstrapWith(currencyDataSet)
.transform(new CurrencyBootstrapFunction());
分区状态 Keyed State #
ProcessFunction 和其他 RichFunction 中的 keyed state 可以用 KeyedStateBootstrapFunction 生成。
public class Account {
public int id;
public double amount;
public long timestamp;
}
public class AccountBootstrapper extends KeyedStateBootstrapFunction<Integer, Account> {
ValueState<Double> state;
@Override
public void open(OpenContext openContext) {
ValueStateDescriptor<Double> descriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor<>("total",Types.DOUBLE);
state = getRuntimeContext().getState(descriptor);
}
@Override
public void processElement(Account value, Context ctx) throws Exception {
state.update(value.amount);
}
}
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Account> accountDataSet = env.fromCollection(accounts);
StateBootstrapTransformation<Account> transformation = OperatorTransformation
.bootstrapWith(accountDataSet)
.keyBy(acc -> acc.id)
.transform(new AccountBootstrapper());
KeyedStateBootstrapFunction 支持设置 event time 定时器和 processing time 定时器。
计时器不会在 state processor API 的 bootstrap 函数内触发,只有在 DataStream 应用程序中恢复后才会激活。
如果设置了 processing time 计时器,但直到该时间过去后状态才恢复,则计时器将在启动后立即触发。
注意 如果您的 bootstrap 函数创建了计时器,则只能使用 process 类型的函数之一来恢复状态。
窗口状态 Window State #
State processor API 支持写出 window operator 的状态。 当写出窗口状态时,需要指定算子 id、窗口分配器、淘汰器(evictor)、触发器(可选)以及聚合类型。 State processor API 中 bootstrap transformation 的配置需要与 DataStream 窗口的配置相匹配。
public class Account {
public int id;
public double amount;
public long timestamp;
}
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Account> accountDataSet = env.fromCollection(accounts);
StateBootstrapTransformation<Account> transformation = OperatorTransformation
.bootstrapWith(accountDataSet)
.keyBy(acc -> acc.id)
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Duration.ofMinutes(5)))
.reduce((left, right) -> left + right);
修改 Savepoint #
除了从头开始创建 savepoint 之外,您还可以基于现有 savepoint 修改,例如为现有作业初始化一个新的算子。
SavepointWriter
.fromExistingSavepoint(env, oldPath, new HashMapStateBackend())
.withOperator(OperatorIdentifier.forUid("uid"), transformation)
.write(newPath);
更改 UID (hashes) #
SavepointWriter#changeOperatorIdenfifier 可以用来修改一个算子的 UIDs 或 UID hash。
如果一个 UID 没有被显式地设置(自动生成的并且是未知的),那么你可以通过提供 UID hash (通过解析 logs 获得 UID hash) 来为算子赋予一个 UID:
savepointWriter
.changeOperatorIdentifier(
OperatorIdentifier.forUidHash("2feb7f8bcc404c3ac8a981959780bd78"),
OperatorIdentifier.forUid("new-uid"))
...
也支持用新的 UID 替换就旧的 UID:
savepointWriter
.changeOperatorIdentifier(
OperatorIdentifier.forUid("old-uid"),
OperatorIdentifier.forUid("new-uid"))
...